A few months ago, I wrote an article explaining that the solution to keeping a budget is as simple (and complex) as maintaining awareness, and I asked you to do two things:
- For 30 days, every time you make a purchase, take three seconds to notice what you spend your money on.
- Send me your stories about your discoveries.
The point was not to change your behavior, or to beat yourself up with what I like to call “the budget stick.” The point was simply to notice.
You sent me a lot of great emails, with some awesome stories about your experiment. Maybe you noticed you spend more money on groceries than you’re comfortable with (or less). Or maybe you discovered that all those little purchases you make on Amazon add up to quite a lot. Either way, for many of you, noticing was just the tip of the iceberg.
Reading through your emails, though, it was pretty clear that a lot of you had the same question: “O.K., what’s next?”
And while I do feel that noticing is an end in and of itself, I wanted to try to address that question. To do so, I’m going to share the story that inspired me to write the article in the first place.
It’s a story about a friend I’ll call Tim.
A few months ago, Tim began making a conscious effort to notice his spending (using a method, in fact, similar to the 30 days and three seconds one). “Coconut water, $3.73,” he would note, “interesting.” That’s it. No judgment, just a quick note, and then he would move on.
The next step Tim took was to enter each item into a spreadsheet. It’s super easy to do and takes less time than you might think (or you can look at your debit or credit card statement).
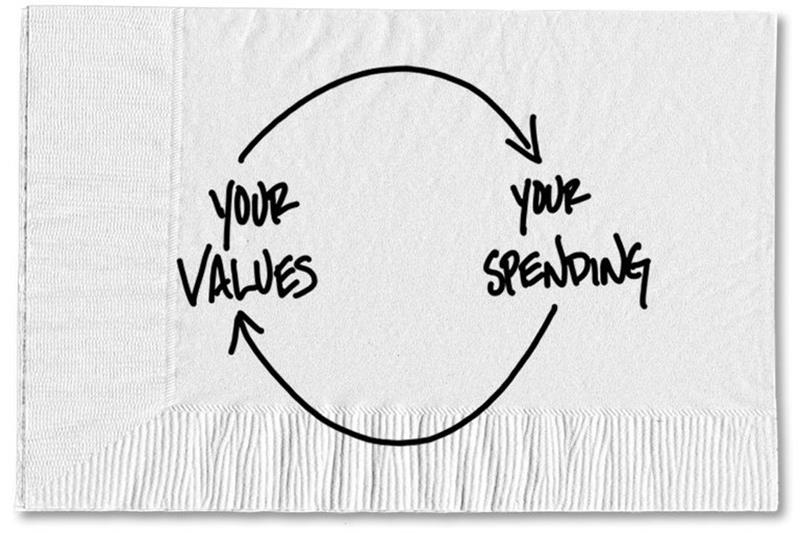
Then, he asked one simple, but powerful, question: “Are these expenditures in line with my values?” He went down the list, item by item, and asked himself, “What was the value this money was invested in and is there a better way I could invest in that value?”
One thing he noticed was a $50 lunch. He recalled that each month, he and a close friend went out for a moderately expensive lunch to catch up. After thinking about it, he realized that the thing he intended to invest in during those lunches was not food or nutrition, but the friendship. And as far as the friendship goes, what he and his buddy really liked to do the most was go hiking, not eat out.
Tim called his buddy and asked how he would feel about changing their monthly lunch meeting to a monthly hike, and the friend was extremely enthusiastic. So no more fancy lunch. Now they make a couple of peanut butter sandwiches and go on a hike instead.
Here’s the really interesting thing. After noticing that there was a better way he could invest in this value of friendship, Tim was able to free up $50 a month to invest in some other value. One of Tim’s values happens to be long-term financial security, so he took that $50 and invested it in an S.&P. 500 index mutual fund.
This may sound a little bit like boring financial adviser talk, but it’s actually quite amazing. Just imagine if I told you that you could have an extra $50 and two hours each month to invest in things you really care about. Would you sign on the dotted line? I bet you would.
This sort of investing behavior is something I like to call values-based budgeting. The whole point of the “30 Days and Three Seconds” experiment is to set yourself up to do this kind of work.
So here are your instructions:
- Step one: notice. Become aware of your expenditures.
- Step two: track. Put your monthly purchases into a spreadsheet.
- Step three: judge. Go through the spreadsheet and ask yourself, “Is this expenditure really in line with my values?”
- Step four: reinvest. When you find places that your spending could be better invested in other values, make the change.
Tim has gotten to the point where he manages his monthly expenditures with surgical precision. Once a month, he and his wife go through their spreadsheet and figure out where they can better invest their money based on their values. And then, every month, I get a text. “Reinvested another $7.50 and 30 minutes!”
Imagine if you did this for two years. That’s $7.50 and 30 minutes a month, times 24 months, which adds up to $180 and 12 hours. How would you like a free $180 and 12 hours a month to invest in things you really care about?
The truth is, it’s yours for the taking. The key though — the secret, really — is awareness. If you don’t take the first step of noticing where your money is disappearing to in the first place, you’ll never find the money and time you could be investing elsewhere.
The above blog is by Carl Richards originally published in The New York Times’ Blog.
About the author: For the last 15 years, Carl Richards has been writing and drawing about the relationship between emotion and money to help make investing easier for the average investor. His first book, “Behavior Gap: Simple Ways to Stop Doing Dumb Things With Money,” was published by Penguin/Portfolio in January 2012. Carl is the director of investor education at BAM Advisor Services. His sketches can be found at behaviorgap.com, and he also contributes to the New York Times Bucks Blog and Morningstar Advisor. You can now buy – “The Behavior Gap” by Carl Richard’s at AMAZON.






0 Comments